Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) affects millions of people across the United States and is one of the most common vascular conditions treated at Aria Vascular. When blood flow to the legs is restricted, patients may experience pain, numbness, slow-healing wounds, or even risk limb loss
Thanks to advances in interventional radiology (IR), many patients can now receive minimally invasive treatment that restores circulation without major surgery. Here’s how IR works—and why it’s becoming the preferred first-line treatment for PAD.
What Is Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)?
Peripheral Artery Disease occurs when plaque—made up of fat, cholesterol, and calcium—builds up inside the arteries of the legs. This narrows the vessels, restricts blood flow, and makes it difficult for oxygen-rich blood to reach the muscles and skin.
PAD is often caused by:
- Atherosclerosis
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- High cholesterol or high blood pressure
PAD affects over 8.5 million Americans, according to the CDC, and is a major cause of reduced mobility and preventable amputations.
Common Symptoms of PAD
Many patients ignore circulation problems until they become severe. Early recognition is essential.
Look out for:
- Leg pain, cramping, or fatigue while walking (claudication)
- Numbness or heaviness in the legs
- Coldness in the feet or toes
- Slow-healing wounds or ulcers
- Loss of hair on the legs
- Pale or discolored skin
If untreated, PAD can progress to Critical Limb Ischemia, a serious condition that threatens limb loss.
How Interventional Radiology Treats PAD
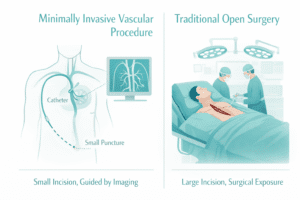
Interventional radiology uses real-time imaging—such as ultrasound, fluoroscopy, or CT guidance—to access blocked arteries using tiny instruments inserted through a pin-sized incision.
This means:
- No major surgery
- No large incisions
- No general anesthesia
- Faster recovery
Blood flow can often be restored in under an hour.
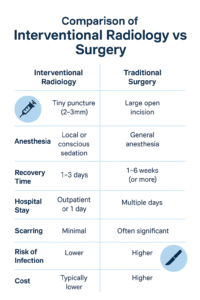
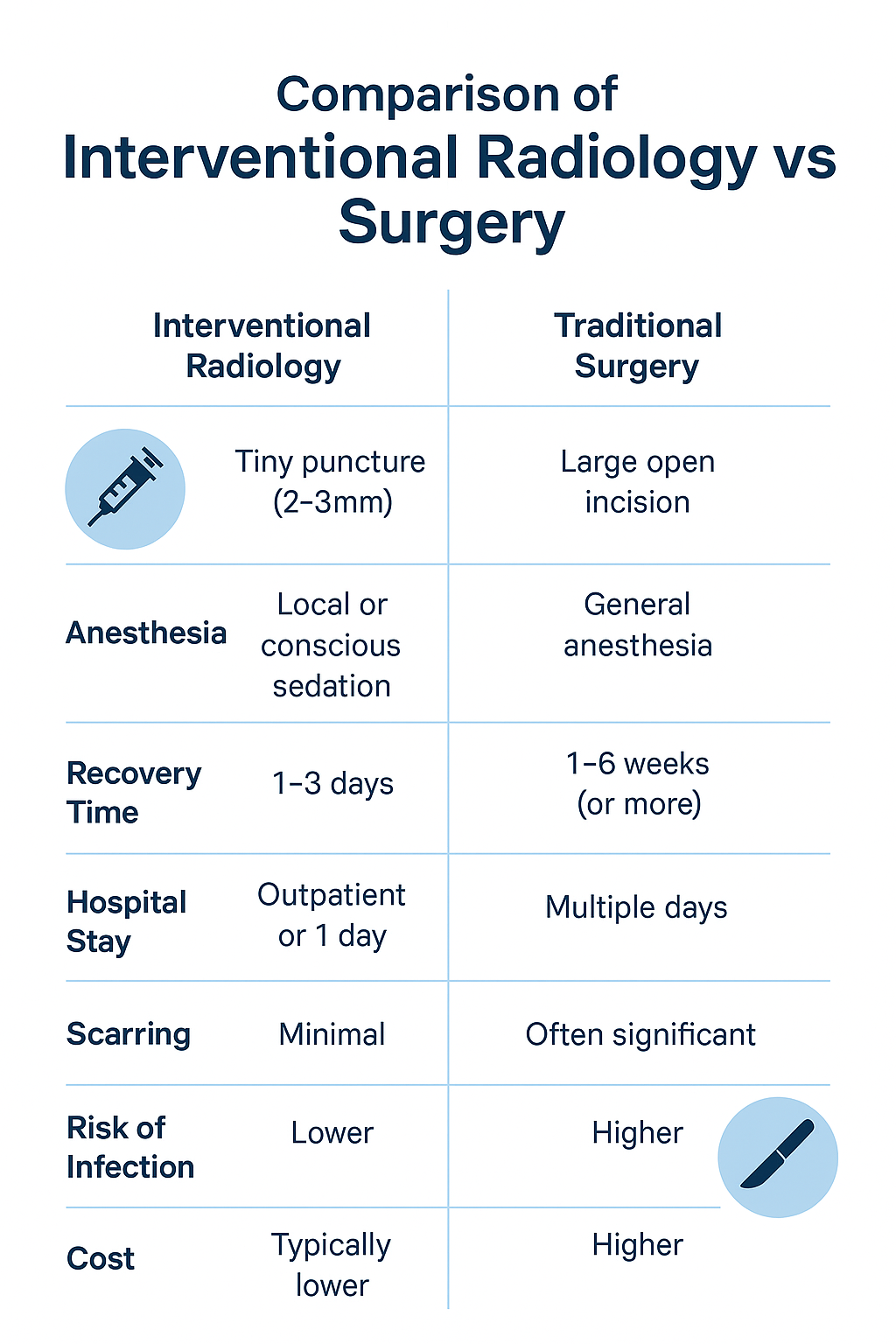
Key Interventional Radiology Procedures for PAD
Feature | Interventional Radiology | Traditional Surgery |
Incision Size | Tiny puncture (2–3mm) | Large open incision |
Anesthesia | Local or conscious sedation | General anesthesia |
Recovery Time | 1–3 days | 1–6 weeks (or more) |
Hospital Stay | Outpatient or 1 day | Multiple days |
Scarring | Minimal | Often significant |
Risk of Infection | Lower | Higher |
Cost | Typically lower | Higher |
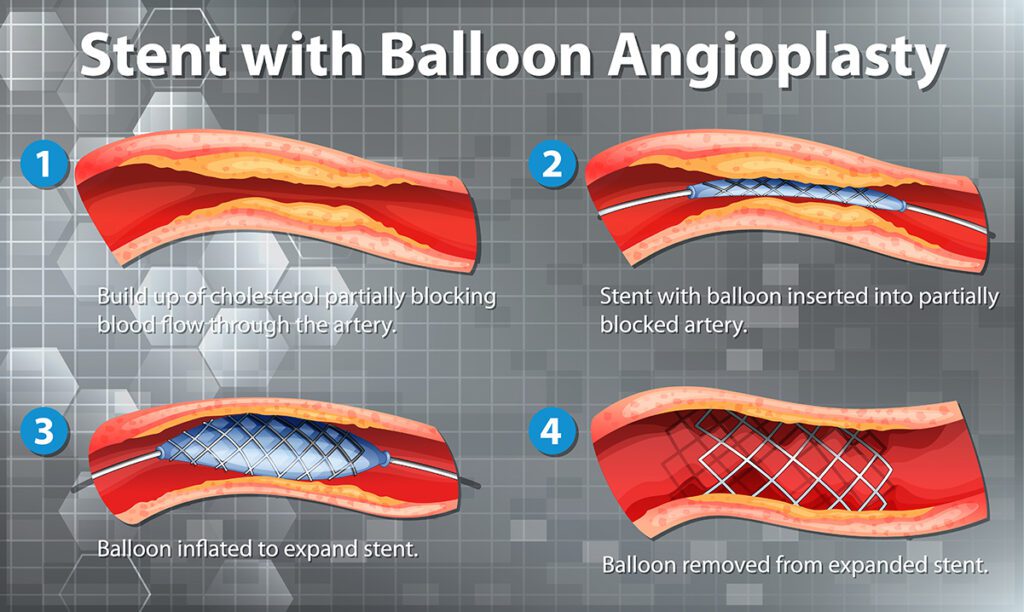
1. Balloon Angioplasty
A small balloon is guided into the narrowed artery and gently inflated to widen the vessel. This restores blood flow and relieves symptoms such as cramping and pain.
Benefits:
- Minimally invasive
- Immediate symptom relief
- Often performed in outpatient settings
2. Stenting
After angioplasty, a stent may be placed to keep the artery open. These mesh-like tubes provide long-term support to weakened or narrowed arteries.
Types of stents:
- Bare-metal stents
- Drug-eluting stents (reduce risk of re-narrowing)
Stents are especially beneficial for multi-segment blockages or recurring PAD.
3. Atherectomy
Atherectomy devices shave, vaporize, or cut away plaque inside arteries. This creates more space for blood flow and may be combined with angioplasty or stenting.
Ideal for patients with severe calcification or long-standing blockages.
Benefits of Interventional Radiology for PAD
Interventional radiology offers several advantages compared to traditional open surgery:
- Tiny puncture instead of a large incision
- Minimal pain
- Local anesthesia only
- Outpatient treatment in most cases
- Walk the same day
- Faster healing and fewer complications
- Excellent long-term success when paired with lifestyle care
For many PAD patients, IR is safer, less invasive, and equally effective.
Interventional Radiology vs. Traditional Surgery for PAD
Open surgery (such as a bypass graft) requires a large incision and a long hospital stay. While it is still necessary for severe or complex disease, interventional radiology is now considered the first-line approach for most patients.
IR Advantages:
- No general anesthesia
- Lower risk of infection
- Quicker recovery
- Cost-effective
- Can be repeated if needed
Most patients prefer IR because it allows them to return to daily life much sooner.
When You Should See a Vascular Specialist
Schedule a vascular evaluation if you experience:
- Leg pain while walking
- Slow-healing or painless foot wounds
- Cold or discolored feet
- Diabetes with circulation concerns
- A history of smoking
Early detection is the key to preventing serious complications.
Why Choose Aria Vascular for PAD Treatment

Aria Vascular is the only comprehensive, multidisciplinary vascular center in San Joaquin County. Our team includes board-certified vascular surgeons and interventional radiologists who specialize in minimally invasive PAD treatment.
What makes us different:
- State-of-the-art endovascular technology
- Full outpatient and inpatient care
- Personalized treatment plans
- Extensive experience in PAD intervention
- Local, accessible care for Stockton, Lodi, Manteca, and Modesto
You don’t need to travel far for world-class vascular care.

Schedule Your PAD Evaluation
PAD doesn’t go away on its own—and early intervention can protect your mobility and long-term health.
🩺 Discover how interventional radiology can help.
Frequently Asked Questions about PAD
Can PAD be treated without surgery?
Yes. Interventional radiology offers minimally invasive treatments like angioplasty and stenting to restore blood flow without open surgery.
How effective is angioplasty for PAD?
Angioplasty is highly effective at relieving leg pain and improving circulation, especially in mild to moderate PAD cases.
How long is recovery after PAD angioplasty or stenting?
Most patients go home the same day and return to normal activities within 24–72 hours.
What are the symptoms that PAD is getting worse?
Increasing leg pain, rest pain, slow-healing ulcers, numbness, and skin discoloration may signal worsening PAD.
When should I see a vascular specialist?
If you have leg pain when walking, non-healing wounds, diabetes, or risk factors like smoking, it’s time for a vascular evaluation.